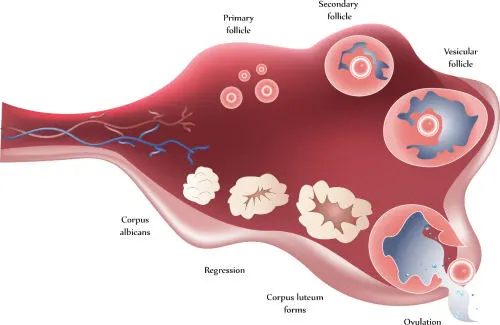
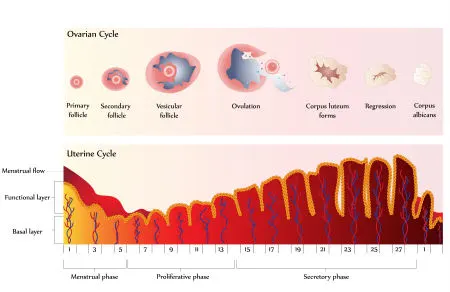
What is Ovulation Induction?
Ovulation induction uses hormonal therapy to stimulate egg development and release. Historically, the use of medication to induce ovulation, commonly called fertility drug, was designed to induce ovulation in women who did not ovulate; typically women with irregular menstrual cycles. The goal of this treatment is to produce a single, healthy egg.
The second use of ovulation induction is to increase the number of eggs reaching maturity in a single cycle to increase chances for conception. This approach is also called super-ovulation or controlled ovarian hyper-stimulation. The key component for this treatment is follicle stimulating hormone, a hormone administered by injection.
Several proprietary brands of follicle stimulating hormones are approved by the F.D.A. in the U.S. Injection with follicle stimulating hormone carries an increased risk of multiple gestation, ovarian hyper-stimulation syndrome, and increased cost and time commitment. Recent evidence suggested there may be an advantage to treating even ovulatory women with fertility medications. These women with “unexplained infertility” may have subtle defects in ovulation and the use of medications may induce the maturity of 2-3 eggs versus only one. This treatment therefore improves the quality and quantity of the ovulation, thus enhancing pregnancy rates.
Ovulation induction, in ovulatory women, is typically combined with intrauterine insemination to maximize cycle success. Ovulation induction should be initiated only after a complete and thorough evaluation for infertility. All underlying hormonal disorders, e.g. thyroid disorder, abnormal prolactin, should be treated prior to resorting to ovulation induction with fertility drugs.
Common Fertility Drugs Used for Ovulation Induction
- Clomiphene Citrate (Seraphene®, Clomid®)
- FSH: follicle stimulating hormone (Follistim®, Gonal-F® and Bravelle®)
- HMG: Human Menopausal Gonadotropin (Repronex®, Menopur®)
- hCG Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (Novarel®, Pregnyl ®or Ovidrel®)
- GnRH Analogues: Leuprolide (Lupron®), Ganirelix® and Cetrotide®
More Information
Clomiphene Citrate (Seraphene®, Clomid®)
Clomiphene citrate is an oral medication that induces ovulation by blocking estrogen receptors. This artificial anti-estrogen effect causes your body to believe estrogen is low and therefore cause the production of more FSH. High to moderate dosage of clomiphene citrate can cause moderate degree of super-ovulation, i.e. the release of multiple eggs in a given menstrual cycle. Some form of monitoring is necessary while taking clomiphene citrate. This monitoring may include ultrasounds, blood estrogen levels, and/or urinary LH testing. Clomiphene citrate, for unexplained infertility is prescribed with intrauterine insemination (IUI). When used for ovulation induction in women who do not ovulate, IUI may not be necessary unless a sperm problem or cervical abnormality is present as well.
FSH: Follicle Stimulating Hormone (Follistim®, Gonal-F® and Bravelle®) & hMG: Human Menopausal Gonadotropin (Repronex®, Menopur®)
FSH is a medication with follicle stimulation hormone while HMG is a medication with a combination of FSH and LH (luteinizing hormone). Both medications are often used together in a single cycle while in some instances one or the other form is more appropriate. They are medications used for stimulation of egg development in women who do not ovulate spontaneously, who fail to ovulate or to conceive with clomiphene citrate, or who ovulate extremely irregularly. It is also used to super-ovulate, to increase the number of eggs developed in a single cycle in women who already ovulate. Due to the variability in response, the dosage varies from individual to individual. Each patient and cycle must be individualized.
FSH and hMG are more potent super-ovulation medications than oral medications such as clomiphene citrate. Hence the risks are higher for severe ovarian hyper-stimulation syndrome and high order multiple pregnancies. Some form of monitoring of the ovarian response is necessary to avoid such complications. A combination of blood estrogen measurement (E2) and ultrasound is the best approach at the present time. These fertility medications can be used with both intrauterine insemination (IUI) and in vitro fertilization (IVF).
FSH and hMG are available only in an injectable form. Self-administered injection techniques are taught in a special injection instruction class given by the nursing staff at the Family Fertility Center. There are also links to injection videos in our website under Resources.
hCG: Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (Novarel®, Pregnyl ®or Ovidrel®)
hCG is a hormone that helps with the final maturation of the eggs and triggers the ovaries to release the mature eggs (ovulation). It also stimulates the corpus luteum to secrete progesterone to prepare the lining of the uterus for implantation of the fertilized egg. Ovulation (follicle rupture) usually occurs about 40-46 hours after the hCG is given. hCG is self-administered as an injection.
GnRH Analogues: Leuprolide (Lupron®), Ganirelix® and Cetrotide®)
Lupron, Ganirelix and Cetrotide are medications that suppress the brain’s secretion of LH and FSH. During ovulation induction or super-ovulation, the higher than natural amount of estrogen produced by the developing follicles may trigger a release of LH before the eggs reach a mature stage, also called premature LH surge. This prevents the immature follicles from further development. GnRH analogues are used to prevent the premature LH surge so as to allow the growing follicles to reach the fully mature stage.
There are several ways to administer GnRH analogue, depending on the characteristics of the individual, the objective of the treatment cycle, i.e. IVF or IUI, and the particular agent selected. Classically, leuprolide is used in the latter part of the menstrual cycle before follicle stimulation with FSH or hMG for IVF treatment. It facilitates the recruitment of a group of follicles synchronized in size and responsiveness to follicle stimulating follicle. It does so by suppressing the selection of a dominant follicle. It also prevents premature ovulation (release of eggs) by preventing LH release. To confirm the effectiveness of the leuprolide treatment, an ultrasound is performed before the ovarian stimulation is begun and a blood estrogen level (E2) may be required. Leuprolide also can be administered in ways other than this classic approach. For example, low dose leuprolide may also be given simultaneously with FSH starting early in the menstrual cycle. This approach is typically used in patients expected to respond slowly or with low number of follicles. Leuprolide is available in an injectable form.
Ganirelix and Cetrotide have immediate effect on the inhibition of the brain’s ability to release FSH and LH. They are typically added after several days of FSH or hMG administration in a super-ovulation cycle for the prevention of premature LH surge.
Schedule a Consultation
Contact Us
If you are experiencing a medical emergency, call 911 or go to the nearest emergency room.
We understand you may have a lot of questions. Additionally, each couple or individual has a unique set of circumstances. To this end, the best way to get answers for your situation is a face-to-face consultation with our physician.
Schedule a Consultation
Contact Us
If you are experiencing a medical emergency, call 911 or go to the nearest emergency room.
We understand you may have a lot of questions. Additionally, each couple or individual has a unique set of circumstances. To this end, the best way to get answers for your situation is a face-to-face consultation with our physician.